Red & Green Iguana
Reptilarium Animals
Red & Green Iguana
Conservation status (Least Concern)
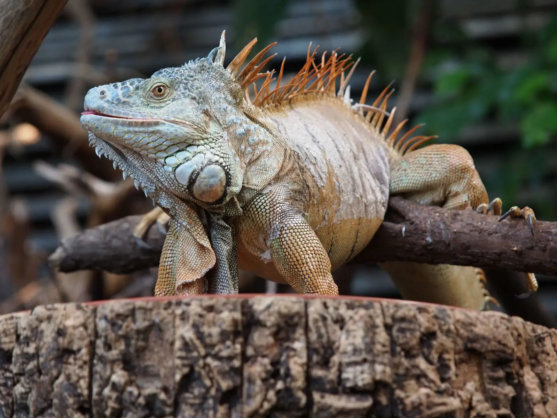




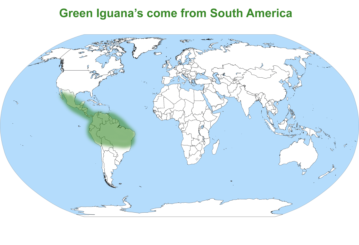
The green iguana (Iguana iguana ), also known as the American iguana or the common green iguana, is a large, arboreal, mostly herbivorous species of lizard of the genus Iguana. Usually, this animal is simply called the iguana. The green iguana ranges over a large geographic area; it is native from southern Brazil and Paraguay as far north as Mexico, and has been introduced from South America to Puerto Rico and is very common throughout the island, where it is colloquially known as gallina de palo ("bamboo chicken" or "chicken of the tree") and considered an invasive species; in the United States, feral populations also exist in South Florida (including the Florida Keys), Hawaii, the U.S. Virgin Islands and the Rio Grande Valley of Texas. Green iguanas have also successfully colonised the island of Anguilla, arriving on the island in 1995 after rafting across the Caribbean from Guadeloupe, where they were introduced.
A herbivore, it has adapted significantly with regard to locomotion and osmoregulation as a result of its diet. It grows to 1.5 m (4.9 ft) in length from head to tail, although a few specimens have grown more than 2 m (6.6 ft) with body weights upward of 20 lb (9.1 kg).
Commonly found in captivity as a pet due to its calm disposition and bright colours, it can be very demanding to care for properly. Space requirements and the need for special lighting and heat can prove challenging to the hobbyist.
The native range of Green iguanas extends from southern Mexico to central Brazil, Dominican Republic, Paraguay, and Bolivia and the Caribbean; specifically Grenada, Aruba, Curaçao, Trinidad, and Tobago, St. Lucia, St. Vincent, and Útila. They have been introduced to Grand Cayman, Puerto Rico, Texas, Florida, Hawaii, and the U.S. Virgin Islands. These lizards inhabit tropical rain forests and are often found near water. They also can be found in other types of habitat including dry forest, gallery forest, and mangroves.
Green iguanas are diurnal, arboreal lizards. They are very agile climbers, and if the lizards fall up to 50 feet (15 m) they can land unhurt (iguanas use their hind leg claws to clasp leaves and branches to break a fall). During cold, wet weather, Green iguanas prefer to stay on the ground for greater warmth. These solitary lizards usually live near water and are excellent swimmers. When swimming, an iguana remains submerged, letting its four legs hang limply against its side. They propel through the water with powerful tail strokes. When iguanas sense danger, they will usually freeze or hide.
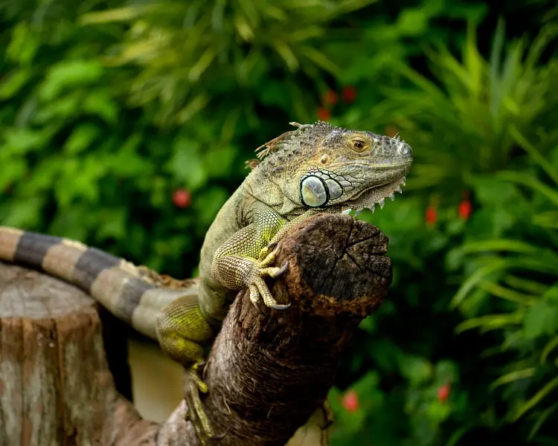

Green iguanas are naturally herbivorous reptiles. They feed on leaves, mustard greens, dandelion greens, flowers, fruit, and growing shoots of upwards of 100 different species of plant. Wild adult Green iguanas may eat birds' eggs, grasshoppers and tree snails.
These beautiful lizards play a very important role in the ecosystem they live in. Due to their diet, Green iguanas are very important as seed disperses. They are also a prey species to the local predators and human. Green iguanas can also indicate changes in the environment because reptiles are more sensitive to environmental changes than humans. So if to watch their responses, people can be warned about possible problems before they become too large.
Fun Facts for Kids
- The word iguana is derived from a Spanish form of the Taíno name for the species: iwana. In some Spanish-speaking countries, males of the species are referred to as "gorrobo" or "ministro" and juveniles are called "iguanita" or "gorrobito".
- In South and Central America, the Green iguana is colloquially known as "gallina de palo" which means "bamboo chicken" or "chicken of the trees".
- Green iguanas have excellent vision, enabling them to detect shapes and motions at long distances. They have cells called “double cone cells” that give these lizards sharp color vision and enable them to see ultraviolet wavelengths. This ability is highly useful when Green iguanas bask in the sun; this way the lizards can ensure that they absorb enough sunlight in the forms of UVA and UVB to produce vitamin D.
- Green iguanas have a white photosensory organ on the top of their heads called the parietal eye. It is also called the third eye, pineal eye or pineal gland. This "eye" cannot form images, but is sensitive to changes in light and dark and can detect movement. This helps the iguana detect predators stalking it from above.
- Green iguanas have very sharp teeth that are capable of shredding leaves and even human skin. These teeth are shaped like a leaf, broad and flat, with serrations on the edge. The teeth are situated on the inner sides of the jawbones, which is why they are hard to see in smaller specimens.
- These lizards can stay underwater for up to 30 minutes.